Search This Blog

Explore Cloud Computing Insights by Dr. Angajala Srinivasa Rao — your trusted destination for comprehensive articles, tutorials, and trends in Cloud Computing, Architectures, Virtualization, IaaS, PaaS, SaaS, Fog & Edge Computing, Cloud Security, and emerging technologies. Get practical guides, real-world examples, and career tips to help students, professionals, and technology enthusiasts stay ahead in the cloud era."
Cloud Computing: Revolutionize Your Business with Efficiency and Flexibility
Are you tired of dealing with the limitations of traditional IT infrastructure? Say goodbye to hardware hassles and embrace the power of cloud computing. With cloud computing, you can take your business to new heights with scalability, efficiency, and flexibility.
- Scalability: Adjust your resources as your needs change.
- Efficiency: Focus on your business, not system maintenance.
- Flexibility: Access your data and apps from anywhere, any time.
- Security: Benefit from robust cloud data protection.
- Cost Savings: Pay only for what you use.
Cloud computing simplifies IT and boosts growth. Let's harness its power.
Featured Post
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
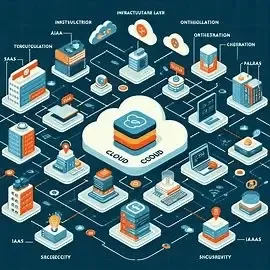
Cloud Computing Architecture
Cloud Computing Architecture
Layers, Components, and Models Explained
Cloud computing architecture is the structural design that enables cloud services to be delivered effectively. It integrates hardware, virtualization, orchestration, and service layers, working together to provide scalable, on-demand resources over the internet.
1. Core Components of Cloud Infrastructure
- Physical Servers: Hardware powering virtual environments.
- Networking: Enables system and user communication.
- Storage: Persistent and scalable data systems.
- Virtualization: Converts physical to virtual resources for efficiency.
2. Key Architectural Layers
2.1 Infrastructure Layer
This foundational layer includes physical servers, data centers, networking, and storage. Virtualization converts physical assets into virtual machines and resources.
2.2 Abstraction Layer
Includes hypervisors and containers (Docker, Kubernetes), enabling the creation of isolated, flexible virtual environments.
2.3 Orchestration and Management
Tools like AWS Console, Azure Portal manage cloud resources. Key functions:
- Resource Management: Dynamic allocation and scaling.
- Service Orchestration: Automates workflows across services.
- Billing & Metering: Tracks usage and generates cost reports.
- Monitoring & Reporting: Ensures availability and performance.
3. Cloud Service Models
- IaaS: Virtual servers, networks, storage (e.g., AWS EC2).
- PaaS: App development platforms (e.g., Google App Engine).
- SaaS: Ready-to-use apps via internet (e.g., Gmail, Salesforce).
4. Deployment Models
- Public Cloud: Third-party infrastructure shared by users.
- Private Cloud: Exclusive for one organization, more secure.
- Hybrid Cloud: Mix of public and private environments.
- Multi-Cloud: Multiple providers for flexibility and risk control.
- Community Cloud: Shared infrastructure for similar needs.
5. Cloud Security & Compliance
- IAM: User access control and authentication.
- Data Security: Encryption and access policies.
- Compliance: Meets industry standards and regulations.
- Disaster Recovery: Backup and restoration for resilience.
Conclusion
Understanding cloud architecture is vital for designing efficient and secure systems. With layers spanning from infrastructure to services, cloud architecture enables scalable, flexible, and reliable digital transformation.
👉 Want to understand the foundation of Cloud Architecture? Read our next post on Basic Concepts of Virtualization to see how virtualization enables the cloud!
✅ SHARE
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Popular Posts

Cloud Computing Definition
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps

Cloud Computing Topics
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Comments
Post a Comment